A In 1992, the devastating collapse of the cod stocks off the East coast of Newfoundland forced the Canadian government to take drastic measures and close the fishery. Over 40,000 people lost their jobs, communities are still struggling to recover and the marine ecosystem is still in a state of collapse. The disintegration of this vital fishery sounded a warning bell to governments around the world who were shocked that a relatively sophisticated, scientifically based fisheries management program, not unlike their own, could have gone so wrong. The Canadian government ignored warnings that their fleets were employing destructive fishing practices and refused to significantly reduce quotas citing the loss of jobs as too great a concern.
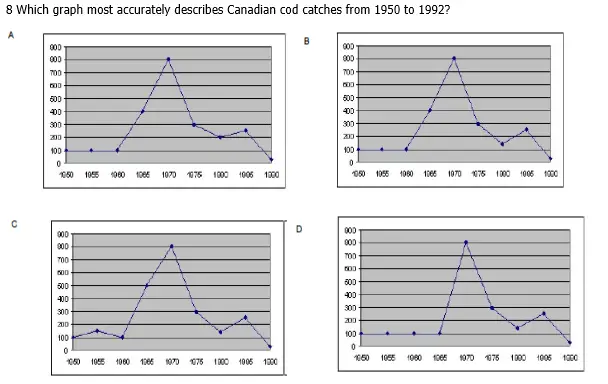
B In the 1950s Canadian and US east coast waters provided an annual 100,000 tons in cod catches rising to 800,000 by 1970. This over fishing led to a catch of only 300,000 tons by 1975. Canada and the US reacted by passing legislation to extend their national jurisdictions over marine living resources out to 200 nautical miles and catches naturally declined to 139,000 tons in 1980. However the Canadian fishing industry took over and restarted the over fishing and catches rose again until, from 1985, it was the Canadians who were landing more than 250,000 tons of northern cod annually. This exploitation ravaged the stocks and by 1990 the catch was so low (29,000 tons) that in 1992 (12%000 tons) Canada had to ban all fishing in east coast waters. In a fishery that had for over a century yielded a quarter-million ton catches, there remained a biomass of less than 1700 tons and the fisheries department also predicted that, even with an immediate recovery, stocks need at least 15 years before they would be healthy enough to withstand previous levels of fishing.
C The devastating fishing came from massive investment poured into constructing huge “draggers”. Draggers haul enormous nets held open by a combination of huge steel plates and heavy chains and rollers that plough the ocean bottom. They drag up anything in the way, inflicting immense damage, destroying critical habitat and contributing to the destabilization of the northern cod ecosystem. The draggers targeted huge aggregations of cod while they were spawning, a time when the fish population is highly vulnerable to capture. Excessive trawling on spawning stocks became highly disruptive to the spawning process and ecosystem. In addition, the trawling activity resulted in a physical dispersion of eggs leading to a higher fertilization failure. Physical and chemical damage to larvae caused by the trawling action also reduced their chances of survival. These draggers are now banned forever from Canadian waters.
D Canadian media often cite excessive fishing by overseas fleets, primarily driven by the capitalist ethic, as the primary cause of the fishing out of the north Atlantic cod stocks. Many nations took fish off the coast of Newfoundland and all used deep-sea trawlers, and many often blatantly exceeded established catch quotas and treaty agreements. There can be little doubt that non North American fishing was a contributing factor in the cod stock collapse, and that the capitalist dynamics that were at work in Canada were all too similar for the foreign vessels and companies. But all of the blame cannot be put there, no matter how easy it is to do, as it does not account for the management of the resources.
E Who was to blame? As the exploitation of the Newfoundland fishery was so predominantly guided by the government, we can argue that a fishery is not a private area, as the fisher lacks management rights normally associated with property and common property. The state had appropriated the property, and made all of the management decisions. Fishermen get told who can fish, what they can fish, and essentially, what to do with the fish once it is caught. In this regard then, when a resource such as the Newfoundland fishery collapses, it is more a tragedy of government negligence than a tragedy of the general public.
F Following the ‘92 ban on northern cod fishing and most other species, an estimated 30 thousand people that had already lost their jobs after the 1992 Northern Cod moratorium took effect, were joined by an additional 12,000 fishermen and plant workers. With more than forty thousand people out of jobs, Newfoundland became an economic disaster area, as processing plants shut down, and vessels from the smallest dory to the monster draggers were made idle or sold overseas at bargain prices. Several hundred Newfoundland communities were devastated.
G Europeans need only look across the North Atlantic to see what could be in store for their cod fishery. In Canada they were too busy with making plans, setting expansive goals, and then allocating fish, and lots of it, instead of making sound business plans to match fishing with the limited availability of the resource. Cod populations in European waters are now so depleted that scientists have recently warned that “all fisheries in this area that target cod should be closed.” The Canadian calamity demonstrates that we now have the technological capability to find and annihilate every commercial fish stock, in any ocean and do irreparable damage to entire ecosystems in the process. In Canada’s case, a two billion dollar recovery bill may only be a part of the total long-term costs. The costs to individuals and desperate communities now deprived of meaningful and sustainable employment is staggering.
Questions 1-6
Reading Passage 1 has 7 paragraphs (A – G). From the list of headings below choose the most suitable headings for paragraphs B – G.
Example Paragraph A iv
List of headings
i Factory Closures
ii The Human Cost
iii The Tragedy of State Mismanagement
iv A Warning to the World
v European Techniques
vi Destructive Trawling Technology
vii Lessons to be Learned
viii The Demise of the Northern Cod
ix Canadian Fishing Limits
x The Breaking of Agreements
xi Foreign Over-fishing
1 Paragraph B
2 Paragraph C
3 Paragraph D
4 Paragraph E
5 Paragraph F
6 Paragraph G
Questions 7-10
Choose the appropriate letters A – D and write them in boxes 7 – 10 on your answer sheet.
7 The Canadian government didn’t want to reduce cod catches pre 1992 because they were worried about
A possible rising unemployment
B the ecological effects
C the marine ecosystem
D drastic measures
8 Which graph most accurately describes Canadian cod catches from 1950 to 1992?
9 According to Reading Passage 1, which of the following is now true about the Newfoundland fisheries?
A Catches of 1700 tons a year only are permitted.
B Normal fishing could start again in 2007.
C No cod fishing is allowed but some other species can be caught.
D Fishing with draggers will be allowed again in 2007.
10 Who does the writer blame for the collapse of the Newfoundland cod fishery?
A The Canadian fishing industry
B The foreign fishing industry
C The Canadian government
D The US fishing industry
Questions 11-14
Do the following statements agree with the views of the writer of the reading passage on Cod in Trouble?
In Boxes 11 – 14 write:
YES if the statement agrees with the writer
NO if the statement doesn’t agree with the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
11 Disruption of cod breeding was a major factor in the Newfoundland cod disaster.
12 Foreign trawlers frequently broke the catch allowances.
13 There was often conflict between the foreign fishermen and the Canadian authorities.
14 Europe does not face the seriousness of the Canadian disaster.
